Trimethoprim: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When you’re dealing with a stubborn urinary tract infection or a bacterial infection that won’t quit, your doctor might reach for trimethoprim, a synthetic antibiotic that blocks bacterial folate production, stopping them from making DNA and multiplying. Also known as the key component in Bactrim, a combination drug with sulfamethoxazole that boosts its effectiveness, trimethoprim doesn’t work alone in most cases—it’s designed to team up. This isn’t just another antibiotic. It’s one of the few that targets bacteria in a way that’s hard for human cells to mimic, which is why it’s been used for decades.
But here’s the catch: trimethoprim only kills bacteria that rely on making their own folate. That means it’s useless against viruses, and it’s not your go-to for every infection. It’s most effective for UTIs, ear infections, bronchitis, and some skin infections. And because it’s often paired with sulfamethoxazole, you’ll see it listed as TMP-SMX on prescriptions. The combo works better than either drug alone, reducing the chance of resistance. But resistance is growing. Overuse in humans and even in livestock has led to strains of bacteria that shrug off trimethoprim like it’s not even there. That’s why doctors are more careful now—they won’t prescribe it unless they’re sure it’s the right tool.
What you might not realize is that trimethoprim doesn’t just affect bacteria. It can also interfere with your body’s ability to use folate, which is why people with certain deficiencies or on other meds like methotrexate need to be watched closely. It’s not dangerous for most, but side effects like rash, nausea, or low blood cell counts can happen. And if you’re pregnant, have kidney issues, or take blood thinners, you need to talk to your doctor first. This isn’t a drug you should grab off the shelf—it’s a prescription for a reason.
What you’ll find in the posts below isn’t just a list of articles about trimethoprim. It’s a collection of real-world stories about how antibiotics like this one fit into bigger systems: patent battles that delay cheaper versions, how generic versions are tested for safety, and why even a simple drug like this can trigger chain reactions in your body or the healthcare system. You’ll see how it connects to C. diff, antibiotic resistance, and even how insurance decides what gets covered. This isn’t just about one pill. It’s about how medicine works—when it helps, when it hurts, and why you need to know the full picture before you take it.
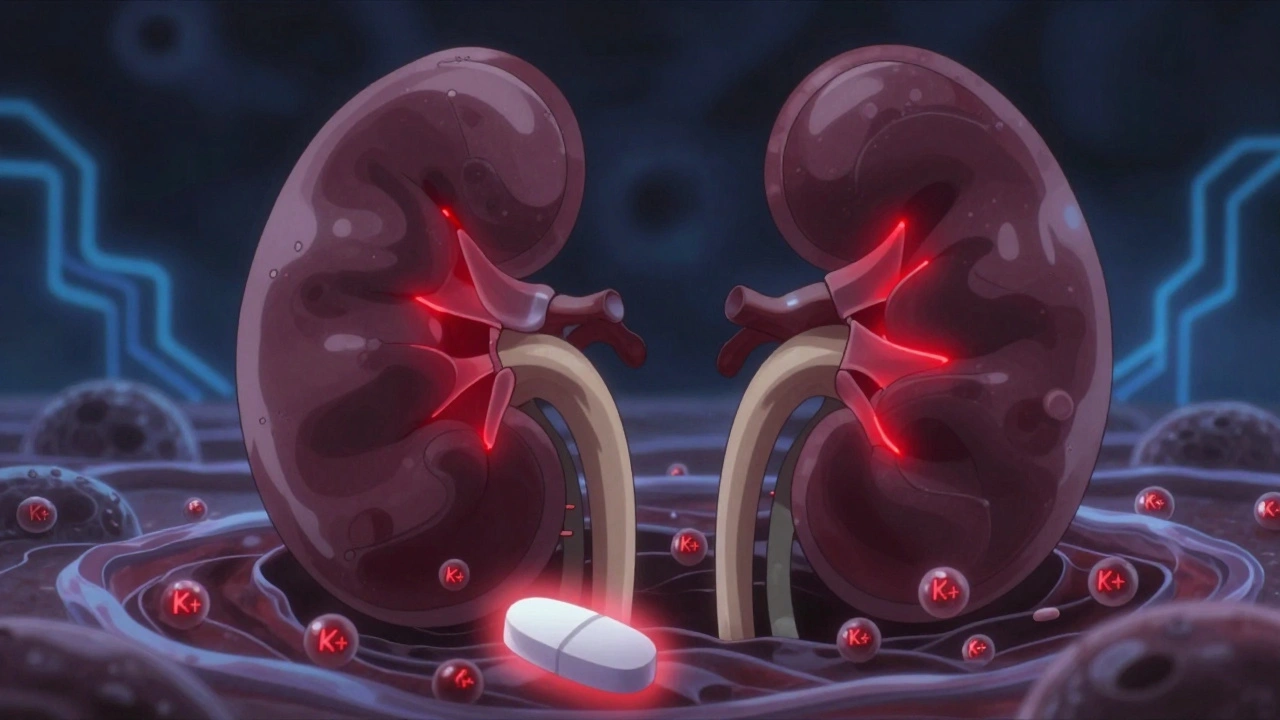
Trimethoprim and Potassium Levels: How This Common Antibiotic Can Raise Your Risk of Hyperkalemia
Trimethoprim, a common antibiotic, can dangerously raise potassium levels - even in people with healthy kidneys. Learn who’s at risk, how fast it happens, and what safer alternatives exist.
learn more